Response of salt-stressed Dolichos lablab L. seedlings to supplementary salicylic acid and its derivalives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53332/sjs.v9i2.160Keywords:
salt-stressed , salicylic acidAbstract
Plants exposed to salinity stress undergo adverse changes in their key physiological and
biochemical parameters. The work reported in this paper assessed the effect of exogenous application
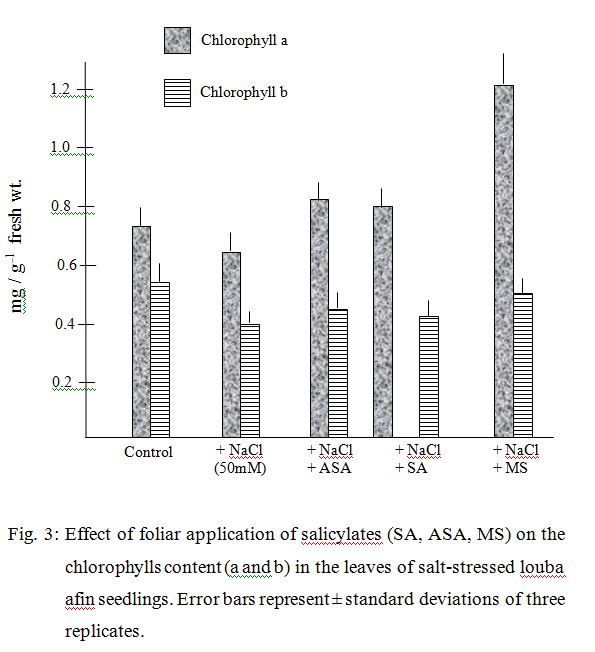
of salicylic acid, acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) and methyl salicylate (5mM each) on proteins, soluble
sugars and chlorophyll content in salt-stressed (50mM NaCl) Dolichos lablab leaves. Salinity significantly
diminished proteins and chlorophylls and increased soluble sugars relative to controls. Exogenous
application of salicylic acid and its derivatives as foliar spray substantially enhanced and alleviated the
deleterious effects of salinity on the studied parameters
Downloads
Published
2021-08-30
Issue
Section
Articles
