Important Anatomical Features In The Taxonomy Of Selected Plant Species From The Genus Ipomoea (Convolvulaceae) In Sudan
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53332/sjs.v9i1.251الكلمات المفتاحية:
Anatomy، Stem، Leaf، Ipomoea، Sudan، Taxonomyالملخص
This paper investigated transverse sections of stems and leaves of seven species belonging to the
genus Ipomoea of the family Convolvulaceae collected from Khartoum state, Sudan. They are
Ipomoea cairica (L.) Sweet, Ipomoea aquatica Forssk, Ipomoea pes-caprae (L.) R. Br., Ipomoae
verticillata Forssk., Ipomoea eriocarpa R. Br., Ipomoea triloba L., and Ipomoea carnea Jacq. The
study revealed that certain features were of significant importance in separation of these taxa. The
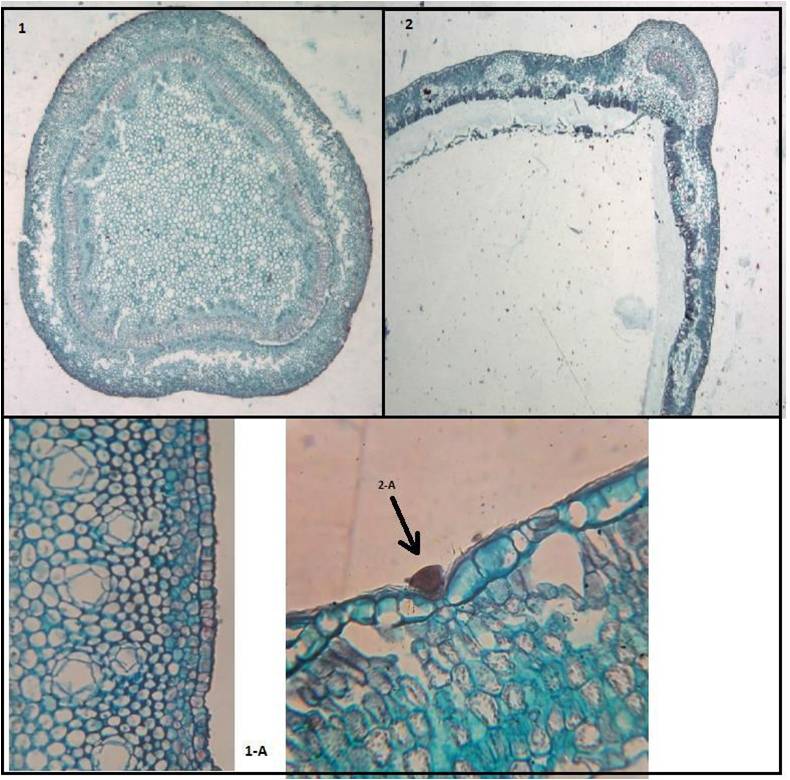
vertically arranged rows of secretory canals separated I. pes-caprae from the other species in which
they are solitary arranged. Also presence of striated stem cuticle separated I. carnea from the other
species which show thin entire cuticle. Hollow pith characterizes I. aquatica while the presence of
crystals in the pith characterizes I. triloba. Two species: I. cairica and I. eriocarpa are characterized
by the presence of sunken glandular hairs on their leaves. I. cairica and I. eriocarpa were
differentiated according to their cambium activity, which was equally active in I. cairica but not in I.
eriocarpa. Laterocytic type of stomata is the common feature among all the studied species